의료가 아닌 공업분야에서 각광을 받아왔던 소재의 박막을 코팅함으로써 병원균과 진균의 세포를 파괴할 수 있는 기술이 개발되었습니다. 이 나노코팅 기술은 항생제가 듣지 않는 약제내성균(슈퍼버그)에도 유효하면서도 인체에 무해하기 때문에, 상처 드레싱 및 의료장비, 임플란트의 소재로서 유망시되고 있습니다.
Broad-Spectrum Solvent-free Layered Black Phosphorus as a Rapid Action Antimicrobial | ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.1c01739
Broad-Spectrum Solvent-free Layered Black Phosphorus as a Rapid Action Antimicrobial
Antimicrobial resistance has rendered many conventional therapeutic measures, such as antibiotics, ineffective. This makes the treatment of infections from pathogenic micro-organisms a major growing health, social, and economic challenge. Recently, nanomat
pubs.acs.org
Superbug Killer: New Nanotech Destroys Bacteria and Fungal Cells, While Leaving Human Cells Unharmed
https://scitechdaily.com/superbug-killer-new-nanotech-destroys-bacteria-and-fungal-cells-while-leaving-human-cells-unharmed/
Superbug Killer: New Nanotech Destroys Bacteria and Fungal Cells, While Leaving Human Cells Unharmed
Nanothin antimicrobial coating could prevent and treat potentially deadly infections. Researchers have developed a new superbug-destroying coating that could be used on wound dressings and implants to prevent and treat potentially deadly bacterial and fung
scitechdaily.com
New Nanothin Coating Kills Superbugs, Fungi, Bacteria: Here's How It Works | Science Times
https://www.sciencetimes.com/articles/30657/20210414/new-nanothin-coating-kills-superbugs-fungi-bacteria-heres-works.htm
New Nanothin Coating Kills Superbugs, Fungi, Bacteria: Here's How It Works
A new nanothin coating material could be added to wound dressings and biomedical implants to prevent and even treat dangerous bacteria and fungi infections - even from the notoriously resistant superbugs.
www.sciencetimes.com
페니실린을 비롯한 항생제는 실용화된 이래 많은 인명을 구해 종종 "20세기의 위대한 발견"의 하나로 꼽힙니다. 그러나 최근 들어 항생제가 듣지 않는 약제내성균이 출현해 의료현장에서는 큰 문제가 되고 있습니다. 세계보건기구(WHO)의 조사에 따르면, 2019년에 약제내성균으로 인해 연간 70만 명이 사망했고, 이대로 새로운 치료법이 개발되지 않으면 사망자 수가 2050년까지 연간 1000만 명으로 증가해 그로 인한 경제적 타격은 세계금융위기와 맞먹는 것으로 추산했습니다.

그래서 오스트레일리아 · 로열멜버른공과대학의 아론 에르본 박사 연구팀은 인의 동소체인 흑린에 주목했습니다. 흑린의 단층막인 phosphorene은 실리콘을 대체할 트랜지스터 및 배터리, 태양전지의 소재로 주목받고 있지만, 산소에 닿으면 빠르게 분해되어 버리기 때문에 취급이 매우 어려운 재료입니다.
이 '산소에 닿으면 빠르게 분해된다'는 성질에 착안한 연구팀은 분해에 의해 발생하는 활성산소를 살균에 응용할 수 있다고 생각하였고, 흑린을 나노미터 단위의 두께의 막으로 만들어 항균효과를 확인하는 실험을 실시했습니다. 그 결과, 대장균과 메티실린 내성 황색포도알균을 포함한 세균 5종과 여러 항진균제에 내성을 나타내는 칸디다 오리스 등 5종류의 진균이 불과 2시간만에 99% 파괴되었습니다.
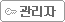
다음은 실험 전후의 대장균을 비교한 현미경 사진입니다. 흑린의 나노코팅에 노출되기 전의 대장균(왼쪽)은 매끈한 원통형이지만 노출된 후의 대장균(오른쪽)은 일그러진 모양이 되며 세포의 내용물이 튀어나와 있는 것을 알 수 있습니다.

세포를 파괴하는 흑린의 효과는 칸디다 오리스에서도 동일했습니다.

흑린 코팅은 세균과 진균 모두에서 높은 효과를 나타낸 반면, 마우스 및 인간의 배양세포에는 전혀 영향을 주지 않았다고 합니다. 또한 실험 시작 후 24시간만에 완전히 분해되어 버렸기 때문에, 인체 나 환경에 미치는 장기적인 영향도 거의 없다고 연구팀은 보고 있습니다.
논문의 공동저자인 사미토 와리아 씨는 "흑린은 산소에 분해되어 버립니다. 이것은 우리와 같은 정밀공학 기술자에게는 골치 아픈 문제였지만, 살균에 이상적인 성질이라는 것을 알게 되었습니다. 즉, 문제가 해결책으로 변신해 버린 것"이라고 말합니다.
연구팀을 이끈 에르본 씨는 "우리가 개발한 나노단위 두께의 코팅은 세균이나 진균의 세포를 찢는데, 이 같은 치명적인 물리적 공격에 대한 방어가 자연적인 진화에 의해 획득되는 데는 수백만 년이 걸릴 것"이라고 예측합니다.
에르본 씨 연구팀은 다양한 살균용 소재의 개발에 노력하고 있으며, 2020년에는 균을 물리적으로 찢어 파괴하는 미세한 액체금속을 발표했습니다.
Antibacterial Liquid Metals: Biofilm Treatment via Magnetic Activation | ACS Nano
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.9b07861
Antibacterial Liquid Metals: Biofilm Treatment via Magnetic Activation
Antibiotic resistance has made the treatment of biofilm-related infections challenging. As such, the quest for next-generation antimicrobial technologies must focus on targeted therapies to which pathogenic bacteria cannot develop resistance. Stimuli-respo
pubs.acs.org
Bacteria shredding tech to fight drug-resistant superbugs - RMIT University
https://www.rmit.edu.au/news/media-releases-and-expert-comments/2020/jan/bacteria-liquid-metal
Bacteria shredding tech to fight drug-resistant superbugs
Researchers have used liquid metals to develop new bacteria-destroying technology that could be the answer to the deadly problem of antibiotic resistance.
www.rmit.edu.au
'생물 & 생명공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 뇌와 고환은 매우 유사한 단백질로 구성되어 있다 (0) | 2021.06.07 |
|---|---|
| 수조 마리의 무리가 지상을 뒤덮는 주기매미 'Brood X'가 우화를 시작 (0) | 2021.05.20 |
| 성인의 주먹보다 거대한 나방 'Endoxyla cinereus'...크기 탓에 잘 날지는 못해 (0) | 2021.05.09 |
| 항생제가 듣지 않는 슈퍼버그가 얼마나 무서운 존재인지 이해를 돕는 동영상 'The Antibiotic Apocalypse Explained' (0) | 2021.05.07 |
| 항생제가 듣지 않는 '슈퍼버그'를 액체금속으로 '물리적으로 찢어 파괴'하는 기술이 발표되다 (0) | 2021.05.04 |
| 식물과 공생하는 균류는 주변 토양의 세균을 모아 이용하고 있다 (0) | 2021.05.03 |
| '고양이는 주인을 사랑하고 있는가?'라는 질문에 대한 전문가의 답변 (0) | 2021.04.20 |
| 세계 최초로 '인간과 원숭이의 키메라' 세포가 실험실에서 탄생...세포분열하며 증식하는 모습도 관찰 (0) | 2021.04.16 |